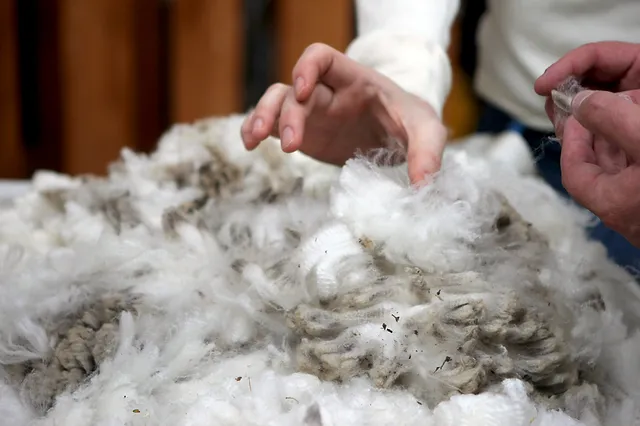
Wool is a natural fiber that is primarily made of protein. It is obtained from the fleece of sheep and certain other animals. The exact composition of wool can vary slightly depending on the animal species, breed, and individual characteristics.
The Science behind Wool
Wool is a remarkable material with unique properties that make it highly suitable for various applications. The science behind wool lies in its structure and composition.
- Structure: Wool fibers have a complex structure that contributes to their exceptional characteristics. Each wool fiber is made up of thousands of protein molecules called keratin, which are arranged in a helical coil structure. This helical structure provides flexibility and resilience to the fiber.
- Moisture absorption: One of wool’s notable properties is its ability to absorb and release moisture. Wool fibers have a high capacity to absorb water vapor from the surrounding environment without feeling wet. This is because wool has a hygroscopic nature, meaning it can absorb moisture without becoming saturated. The structure of wool fibers allows them to trap and hold moisture within the fiber core, keeping the surface dry.
- Insulation: Wool provides excellent insulation. The crimped structure of wool fibers creates air pockets within the fabric. These air pockets act as insulators, trapping warm air close to the body and preventing heat loss. This natural insulation makes wool garments comfortable to wear in both cold and warm climates.
- Elasticity and resilience: Wool fibers have a natural elasticity that allows them to stretch and recover their shape. This property enables wool garments to withstand stretching and bending without losing their form. Wool fibers also have excellent resilience, meaning they can return to their original shape after being stretched or compressed.
- Fire resistance: Wool is naturally flame retardant. It has a high ignition temperature and does not melt or stick to the skin like synthetic fibers. When exposed to flame, wool forms a protective char layer that acts as a barrier, slowing down the spread of fire.
- Odor resistance: Wool has inherent odor-resistant properties. The chemical structure of wool allows it to absorb and neutralize odors, keeping garments fresh even after prolonged use.
From Sheep to Wool: The Production Process
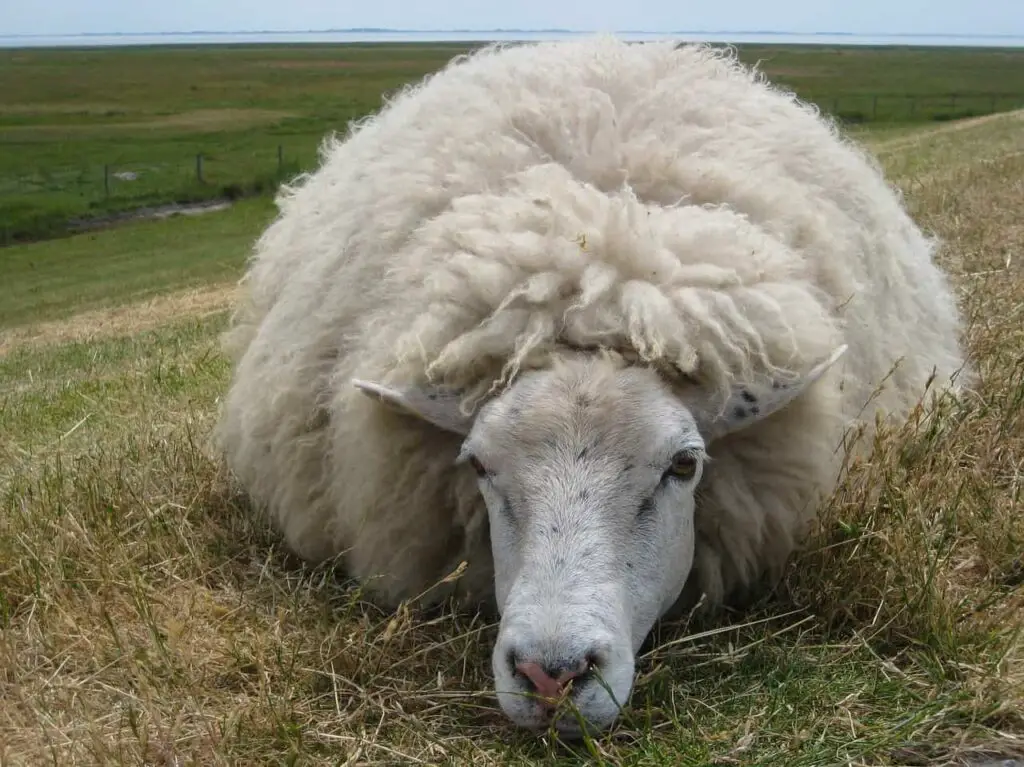

The production process of wool involves several steps, starting from the rearing of sheep to the processing of their fleece into usable wool. Here is an overview of the production process, explained in points:
- Sheep rearing:
Sheep are raised on farms, where they graze on pastures and receive appropriate care and nutrition.
Sheep are sheared once or twice a year to obtain their wool. Shearing is done by skilled shearers using electric clippers to carefully remove the fleece.
- Skirting and sorting:
After shearing, the fleece is carefully spread out and inspected. The process of skirting involves removing any undesirable parts like dirty or matted sections.
The fleece is then sorted based on various factors, such as fiber length, fineness, color, and quality. This step helps in segregating the wool for different applications.
- Washing:
The sorted fleece is thoroughly washed to remove impurities such as dirt, grease, sweat, and vegetable matter. This process is known as scouring.
Specialized detergents and gentle agitation are used to clean the wool without causing damage. After washing, the wool is rinsed and dried.
- Carding:
Carding is the process of aligning and separating the individual wool fibers. It helps to remove any remaining impurities and create a more uniform web of fibers.
Traditional carding involves using handheld or mechanical carding brushes, while modern methods employ specialized carding machines.
- Spinning:
Spinning is the process of twisting the carded wool fibers together to create yarn. It can be done by hand using a spinning wheel or by using mechanical spinning machines.
The spinning process imparts strength and durability to the wool fibers, making them suitable for weaving or knitting.
- Weaving or knitting:
The spun wool yarn is further processed through weaving or knitting machines to create various woolen fabrics or knitted garments.
Weaving involves interlacing the yarns at right angles to form a fabric, while knitting involves interlocking loops of yarn to create a flexible textile.
- Finishing:
After weaving or knitting, the woolen fabric undergoes finishing processes to enhance its properties and appearance.
This may include treatments like dyeing, steaming, brushing, and pressing to achieve the desired color, texture, and finish.
- Product manufacturing:
The finished woolen fabric or knitted wool is then used for manufacturing various products such as clothing, blankets, carpets, and upholstery.
Skilled artisans and manufacturers transform the wool into final products through cutting, sewing, and other techniques.
- Distribution and retail:
The woolen products are distributed to wholesalers, retailers, and consumers through various channels, including textile companies, specialty stores, and online platforms.
Consumers can purchase woolen products for personal use, enjoying the warmth, comfort, and other benefits of this natural fiber.
The Versatility of Wool
Wool is an incredibly versatile material that finds applications in various industries. Its unique properties make it highly desirable for a wide range of products. Here are some of the key areas where wool showcases its versatility:
Clothing and Fashion:
- Wool is extensively used in the production of clothing and fashion items. It is known for its exceptional insulation properties, keeping the body warm in cold weather.
- Wool garments are breathable and moisture-wicking, allowing for comfort in different climates and activities.
- Wool fibers are naturally elastic and can retain their shape, making them ideal for tailored clothing and garments that require drape and resilience.
- The versatility of wool extends to fashion accessories like scarves, hats, and gloves, where its warmth and style are valued.
Home and Interiors:
- Wool is utilized in home textiles, including blankets, throws, upholstery, and carpets. It provides a luxurious feel, warmth, and durability.
- Wool carpets and rugs are highly sought after for their natural beauty, noise reduction qualities, and ability to trap allergens.
- Wool is also used in bedding products such as mattresses, mattress toppers, and pillows due to its breathability and moisture-wicking properties, promoting a comfortable sleep environment.
Outdoor Gear and Sports:
- Wool is commonly employed in outdoor and sportswear due to its excellent insulation, moisture management, and odor-resistant properties.
- Outdoor enthusiasts rely on wool garments, socks, and base layers to regulate body temperature, even when exposed to changing weather conditions.
- Wool’s natural resistance to odors makes it suitable for high-performance sportswear that can endure prolonged use without developing unpleasant smells.
Insulation and Filtration:
- Wool’s crimped structure creates air pockets that make it an effective insulating material. It is used in the production of thermal insulation for buildings and homes.
- Wool is also utilized in filtration applications, such as air and water filters, due to its ability to trap particles and pollutants while allowing airflow.
Industrial and Technical Applications:
- Wool fibers are employed in industrial applications, including polishing and buffing materials, as they can provide a gentle yet effective abrasive surface.
- In the automotive industry, wool is used in vehicle interiors for its sound-dampening properties, reducing noise and enhancing passenger comfort.
- Wool is being explored for innovative technical applications, such as in the development of eco-friendly and sustainable materials, including biodegradable plastics and composites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wool is a remarkable natural material with a multitude of applications, showcasing its versatility across various industries. From clothing and fashion to home textiles, outdoor gear, and industrial uses, wool offers unique properties that make it highly sought after.
References:
https://www.woolmark.com/fibre/woolgrowers/where-wool-comes-from/